ERP for Dummies: A Comprehensive Guide to Enterprise Resource Planning
Introduction
In today’s competitive business landscape, organizations are constantly seeking ways to streamline their operations, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have emerged as a powerful tool to address these challenges, offering a comprehensive solution for managing various aspects of a business. However, for those unfamiliar with ERP, navigating the complexities of these systems can be daunting. This guide aims to demystify ERP for dummies, providing a comprehensive overview of its benefits, key features, and implementation considerations.
Understanding ERP: A Centralized Hub for Business Data
ERP systems serve as a central repository for all critical business data, including financial information, customer relationship management (CRM), supply chain management, and human resources. By integrating these disparate data sources, ERP provides a holistic view of the organization, enabling real-time decision-making and improved collaboration across departments.
Key Benefits of ERP: Streamlining Operations and Enhancing Efficiency
ERP systems offer a multitude of benefits for businesses of all sizes. These include:
- Streamlined Processes: ERP automates and standardizes business processes, eliminating redundancies and improving efficiency.
- Improved Data Accuracy: Centralizing data in a single system ensures data integrity and consistency, reducing errors and improving decision-making.
- Enhanced Collaboration: ERP facilitates seamless communication and collaboration between departments, breaking down silos and fostering a more cohesive work environment.
- Increased Productivity: Automated workflows and improved data accessibility empower employees to work more efficiently, freeing up time for strategic initiatives.
- Reduced Costs: ERP systems can significantly reduce operational costs through process optimization, inventory management, and improved supply chain efficiency.
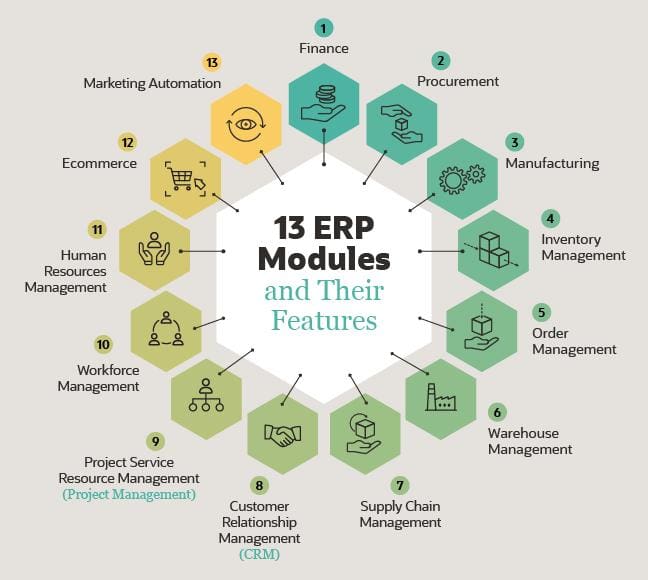
Core Features of ERP: A Comprehensive Suite of Business Management Tools
ERP systems encompass a wide range of features designed to meet the specific needs of businesses. These core features include:
- Financial Management: ERP systems provide robust financial management capabilities, including general ledger, accounts payable/receivable, and budgeting.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): ERP systems enable businesses to manage customer interactions, track sales opportunities, and provide personalized customer service.
- Supply Chain Management: ERP systems optimize supply chain processes, including inventory management, order fulfillment, and supplier relationships.
- Human Resources Management: ERP systems streamline HR functions, including payroll processing, benefits administration, and employee performance management.
- Project Management: ERP systems provide tools for project planning, tracking, and resource allocation, enabling efficient project execution.
/userfiles/images/SAP-ERP.jpg)
Implementation Considerations: Planning for a Successful ERP Deployment
Implementing an ERP system is a complex undertaking that requires careful planning and execution. Key considerations include:
- Business Process Analysis: A thorough analysis of existing business processes is essential to identify areas for improvement and ensure a smooth transition to the ERP system.
- Vendor Selection: Choosing the right ERP vendor is crucial. Consider factors such as industry expertise, product capabilities, and implementation track record.
- Project Management: Effective project management is essential to ensure timely and successful implementation, with clear timelines, milestones, and communication channels.
- Data Migration: Migrating data from legacy systems to the ERP system requires careful planning and data cleansing to ensure accuracy and integrity.
- User Training: Comprehensive user training is essential to ensure adoption and maximize the benefits of the ERP system.

Advantages and Disadvantages of ERP: Weighing the Pros and Cons
ERP systems offer significant advantages, but it’s important to consider potential drawbacks as well.
Advantages:
- Improved Efficiency: ERP streamlines processes, reduces redundancies, and enhances productivity.
- Enhanced Data Quality: Centralized data improves accuracy, consistency, and decision-making.
- Increased Collaboration: ERP facilitates seamless communication and collaboration across departments.
- Reduced Costs: ERP optimizes operations, reduces inventory waste, and improves supply chain efficiency.
- Scalability: ERP systems are designed to grow with businesses, supporting future expansion and changing needs.
Disadvantages:
- High Implementation Costs: ERP systems can be expensive to implement, requiring significant upfront investment.
- Complexity: ERP systems are complex and require specialized knowledge for implementation and ongoing maintenance.
- Data Security Concerns: Centralizing data in a single system raises potential security risks that need to be addressed.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist changes to existing processes, requiring effective change management strategies.
- Ongoing Maintenance: ERP systems require ongoing maintenance and updates to ensure optimal performance.
Summary: Key Takeaways about ERP for Dummies
ERP systems offer a comprehensive solution for managing business operations, providing numerous benefits such as improved efficiency, enhanced data quality, increased collaboration, reduced costs, and scalability. However, it’s important to consider potential drawbacks, including high implementation costs, complexity, data security concerns, resistance to change, and ongoing maintenance requirements. Careful planning, vendor selection, project management, data migration, and user training are essential for successful ERP implementation.
Frequently Asked Questions about ERP for Dummies
1. What is the primary purpose of an ERP system?
ERP systems provide a centralized platform for managing all aspects of a business, including financial management, customer relationships, supply chain operations, and human resources.
2. What are the key benefits of using an ERP system?
ERP systems offer numerous benefits, including streamlined processes, improved data accuracy, enhanced collaboration, increased productivity, and reduced costs.
3. What are the core features typically found in an ERP system?
Core ERP features include financial management, customer relationship management (CRM), supply chain management, human resources management, and project management.
4. How does an ERP system improve data quality?
ERP systems centralize data from disparate sources, ensuring data integrity, consistency, and accuracy.
5. How does an ERP system enhance collaboration?
ERP systems facilitate seamless communication and collaboration between departments by providing a shared platform for data access and information exchange.
6. What are the potential drawbacks of implementing an ERP system?
ERP implementation can be complex and expensive, and it may require significant changes to existing business processes.
7. What is the role of a project manager in ERP implementation?
A project manager is responsible for overseeing the implementation process, ensuring timely delivery, adherence to budget, and successful adoption of the ERP system.
8. What is data migration and why is it important in ERP implementation?
Data migration involves transferring data from legacy systems to the new ERP system. It is critical to ensure data accuracy and integrity during migration.
9. How can organizations overcome resistance to change during ERP implementation?
Effective change management strategies, including clear communication, user training, and stakeholder involvement, can help overcome resistance to change.
10. What is the importance of ongoing maintenance for ERP systems?
Ongoing maintenance is essential to ensure optimal performance, security updates, and alignment with evolving business needs.
11. How can organizations measure the return on investment (ROI) of an ERP system?
ROI can be measured by quantifying improvements in efficiency, productivity, cost savings, and customer satisfaction.
12. What are some industry-specific considerations for ERP implementation?
ERP systems can be tailored to meet the specific needs of different industries, such as manufacturing, healthcare, and retail.
13. How can organizations ensure data security in an ERP system?
Implementing robust security measures, including access controls, encryption, and regular security audits, is essential to protect data from unauthorized access.
Conclusion: Embracing ERP for Business Transformation
ERP systems have become indispensable tools for businesses seeking to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. By providing a comprehensive solution for managing all aspects of an organization, ERP systems empower businesses to make informed decisions, enhance collaboration, and achieve operational excellence.
While ERP implementation can be a complex undertaking, the potential benefits far outweigh the challenges. By carefully planning, selecting the right vendor, and following best practices for implementation, organizations can harness the power of ERP to transform their businesses and unlock new levels of success.
Closing Statement: A Call to Action
If you’re ready to take your business to the next level, embrace ERP as a strategic investment in your future. The benefits of ERP are undeniable, and the time to act is now. Contact a reputable ERP vendor today to schedule a consultation and learn how ERP can revolutionize your operations and drive your business towards unprecedented growth.