The Average Number of People in a School: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
The average number of people in a school is a crucial metric that can influence various aspects of educational planning and resource allocation. Understanding this number provides insights into the scale and complexity of educational institutions, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions about facilities, staffing, and curriculum. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of average school population, exploring its implications for educational practices and outcomes.
Defining Average School Population
The average school population refers to the typical number of individuals associated with an educational institution, including students, faculty, staff, and administrators. It is calculated by dividing the total number of people affiliated with the school by the number of schools in a given area or region.
Factors Influencing School Population
Several factors contribute to the variation in school population across different institutions and geographical locations. These include:
- School size: Larger schools typically have higher student populations than smaller schools.
- Grade levels: Elementary schools generally have lower student populations than secondary schools.
- Location: Schools in densely populated areas tend to have larger populations than those in rural areas.
- Socioeconomic factors: Schools in affluent areas often have lower student populations than those in disadvantaged communities.
- Educational policies: Government policies and regulations can influence school population size by affecting enrollment rates and class sizes.
Average School Population in the United States
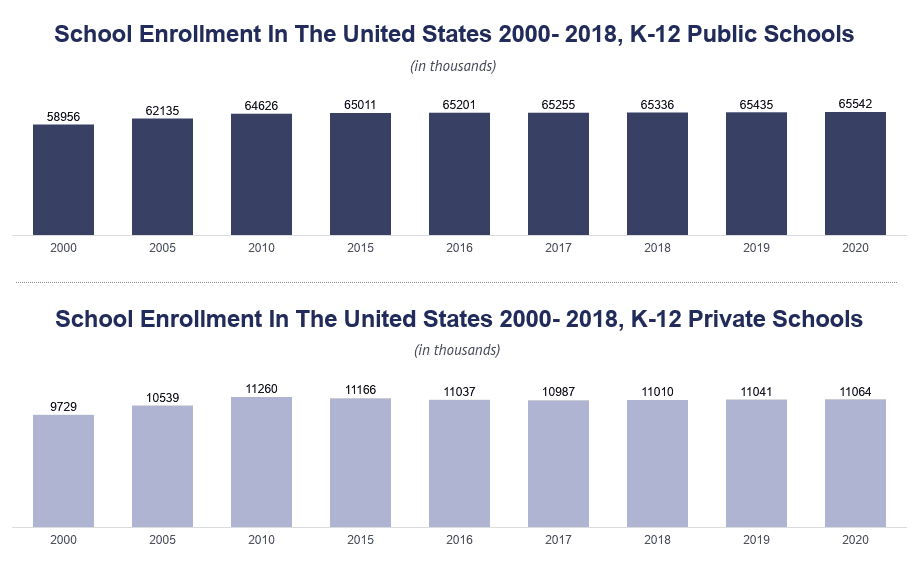
According to the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), the average public school population in the United States during the 2021-2022 school year was approximately 500 students. However, this number varies significantly across states and school districts.
Advantages of a Smaller School Population
- Increased individualized attention: Smaller schools allow teachers to provide more personalized instruction and support to students.
- Enhanced student-teacher relationships: Students in smaller schools often have stronger bonds with their teachers, fostering a more supportive learning environment.
- Improved academic outcomes: Research suggests that students in smaller schools tend to perform better academically than those in larger schools.
- Greater sense of community: Smaller schools foster a closer sense of community among students, staff, and parents.
- Reduced administrative costs: Schools with smaller populations may require fewer administrative staff and resources.

Disadvantages of a Smaller School Population
- Limited course offerings: Smaller schools may not be able to offer the same range of courses as larger schools.
- Fewer extracurricular activities: Schools with smaller populations may have fewer extracurricular activities and clubs for students to participate in.
- Less diversity: Smaller schools may have less diversity in terms of student backgrounds and experiences.
- Transportation challenges: Students in rural areas with smaller schools may face transportation challenges due to longer distances to school.
- Limited access to specialized resources: Smaller schools may not have access to specialized resources such as advanced technology or specialized teachers.

Average School Population and Educational Outcomes
Research has shown that school population size can impact educational outcomes. Studies suggest that students in smaller schools tend to have higher academic achievement, better social-emotional development, and greater college attendance rates. However, it is important to note that school population size is just one factor that influences educational outcomes, and other factors such as school leadership, teacher quality, and socioeconomic status also play a significant role.
Planning for School Population Growth
As communities grow and change, it is essential for school districts to plan for future school population growth. This involves forecasting enrollment trends, identifying potential overcrowding issues, and developing strategies to accommodate additional students. Failure to plan for population growth can lead to overcrowding, inadequate facilities, and decreased educational quality.
Summary
The average number of people in a school is a multifaceted metric that provides valuable insights into the size and complexity of educational institutions. Understanding the factors that influence school population, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of different population sizes, is crucial for educational planning and resource allocation. By carefully considering the implications of school population size, stakeholders can create optimal learning environments that support student success.
Q&As
-
What is the average school population in the United States?
- Approximately 500 students in public schools during the 2021-2022 school year.
-
What are the advantages of a smaller school population?
- Increased individualized attention, enhanced student-teacher relationships, improved academic outcomes, greater sense of community, and reduced administrative costs.
-
What are the disadvantages of a smaller school population?
- Limited course offerings, fewer extracurricular activities, less diversity, transportation challenges, and limited access to specialized resources.
-
How does school population size impact educational outcomes?
- Research suggests that students in smaller schools tend to have higher academic achievement, better social-emotional development, and greater college attendance rates.
-
What factors influence school population size?
- School size, grade levels, location, socioeconomic factors, and educational policies.
-
Why is it important to plan for school population growth?
- To avoid overcrowding, ensure adequate facilities, and maintain educational quality.
Conclusion
Understanding the average number of people in a school is essential for effective educational planning and decision-making. By considering the factors that influence school population, the advantages and disadvantages of different population sizes, and the impact on educational outcomes, stakeholders can create optimal learning environments that foster student success. It is imperative for schools to adapt to changing population trends and ensure that all students have access to high-quality educational opportunities.
Closing Statement
The average number of people in a school is a dynamic metric that reflects the evolving needs of our educational system. By embracing a comprehensive understanding of this metric, we can empower schools to create inclusive and supportive learning environments that prepare all students for future success.
