Financial Assistance: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Its Meaning and Implications
Financial assistance refers to various forms of monetary aid provided to individuals or organizations in need. It encompasses a wide range of programs and services designed to alleviate financial burdens, promote economic stability, and foster social well-being. Understanding the meaning and implications of financial assistance is crucial for navigating the complexities of accessing and utilizing these resources effectively.
Defining Financial Assistance
Financial assistance encompasses a diverse array of programs, each with specific eligibility criteria and application processes. These programs can be categorized into two primary types:
-
Government Assistance: Provided by federal, state, and local government agencies, government assistance programs are typically need-based and aim to support low-income individuals and families. Examples include welfare benefits, food stamps, and housing assistance.
-
Non-Government Assistance: Offered by non-profit organizations, charities, and private foundations, non-government assistance programs provide financial aid to individuals and organizations based on specific criteria, such as income level, disability status, or educational goals. Scholarships, grants, and emergency assistance are common examples.
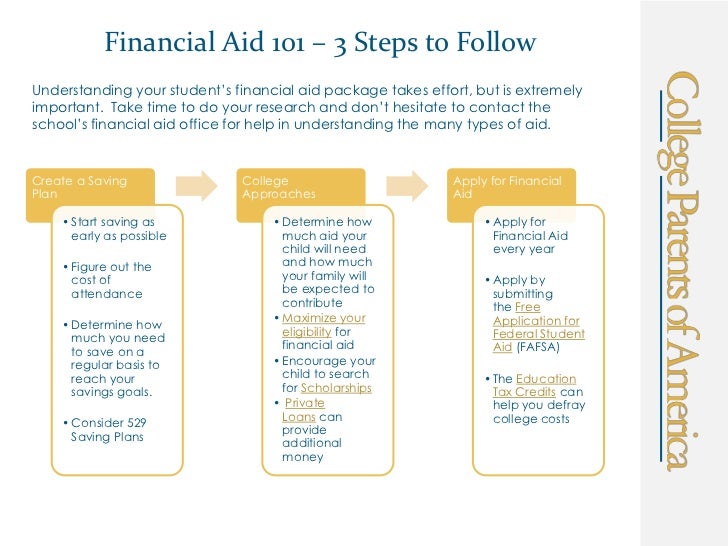
Purpose and Benefits of Financial Assistance
Financial assistance serves multiple purposes, including:
-
Alleviating Financial Hardship: Financial assistance provides immediate relief from financial distress, helping individuals and families meet basic needs such as food, shelter, and healthcare.
-
Promoting Economic Stability: By providing financial support, assistance programs help individuals and families stabilize their financial situation, reducing the risk of homelessness, poverty, and other economic challenges.
-
Fostering Social Well-Being: Financial assistance contributes to social well-being by addressing the underlying causes of poverty and inequality, promoting access to education, healthcare, and other essential services.

Types of Financial Assistance
The specific types of financial assistance available vary depending on the provider and the target population. Some common types include:
-
Cash Assistance: Direct cash payments provided to individuals or families to meet basic needs or cover specific expenses.

-
In-Kind Assistance: Non-cash assistance provided in the form of goods or services, such as food stamps, housing vouchers, or healthcare coverage.
-
Educational Assistance: Financial aid programs that support students in pursuing higher education, including scholarships, grants, and loans.
-
Emergency Assistance: Short-term financial aid provided to individuals or families facing unexpected financial crises, such as natural disasters or job loss.
Eligibility and Application Process
Eligibility for financial assistance programs varies widely depending on the specific program and provider. In general, programs consider factors such as income level, household size, disability status, and educational goals. The application process typically involves completing an application form and providing supporting documentation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Financial Assistance
Advantages:
-
Immediate Financial Relief: Financial assistance provides immediate financial support to individuals and families in need, alleviating financial stress and improving their quality of life.
-
Promotes Economic Stability: By stabilizing individuals’ financial situations, assistance programs help reduce the risk of poverty, homelessness, and other economic challenges.
-
Fosters Social Well-Being: Financial assistance contributes to social well-being by addressing the underlying causes of poverty and inequality, promoting access to essential services.
Disadvantages:
-
Dependency Concerns: Some critics argue that financial assistance programs can create dependency on government or non-profit organizations, discouraging individuals from seeking employment or becoming self-sufficient.
-
Limited Availability: Financial assistance programs often have limited funding and strict eligibility criteria, which can make it difficult for some individuals to access the support they need.
-
Potential for Fraud: Financial assistance programs can be vulnerable to fraud and abuse, which can divert resources away from those who genuinely need assistance.
Conclusion: The Importance of Financial Assistance
Financial assistance plays a vital role in alleviating financial hardship, promoting economic stability, and fostering social well-being. By understanding the meaning, types, eligibility criteria, and potential advantages and disadvantages of financial assistance, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions about accessing and utilizing these resources effectively. Financial assistance programs are essential safety nets that help individuals and families navigate financial challenges and achieve their full potential.
