Eco-Friendly Home Floor Plans: Building Sustainable and Stylish Living Spaces
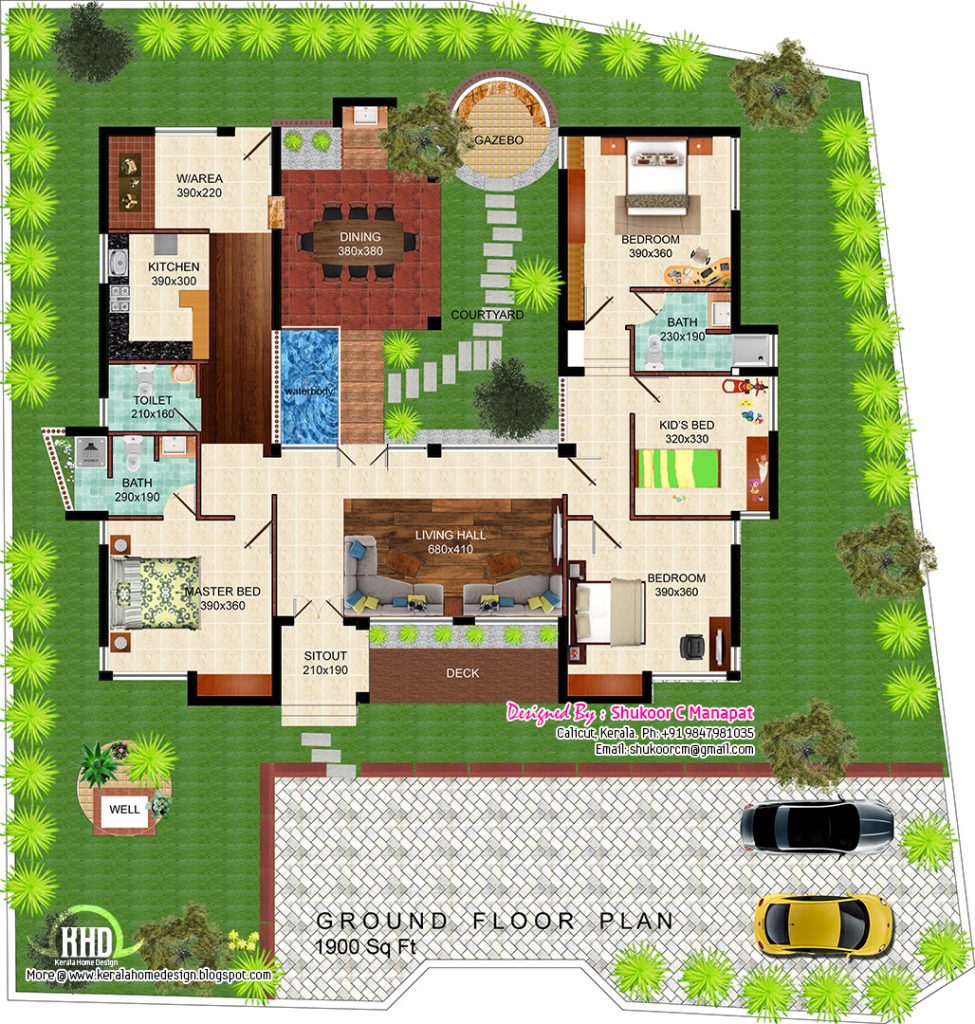
Introduction:
In a world increasingly concerned with environmental sustainability, the design and construction of our homes have taken center stage. Eco-friendly home floor plans are no longer a niche concept; they represent a fundamental shift in how we approach architecture and interior design. This comprehensive guide explores the core principles, benefits, and practical considerations of incorporating eco-friendly elements into your home’s blueprint, empowering you to build a sustainable and stylish living space.
The Essence of Eco-Friendly Home Floor Plans:

Eco-friendly home floor plans go beyond aesthetics; they prioritize environmental responsibility, energy efficiency, and resource conservation. They embody a holistic approach to design, considering the impact of every architectural choice on the planet and its inhabitants.
Core Premise:
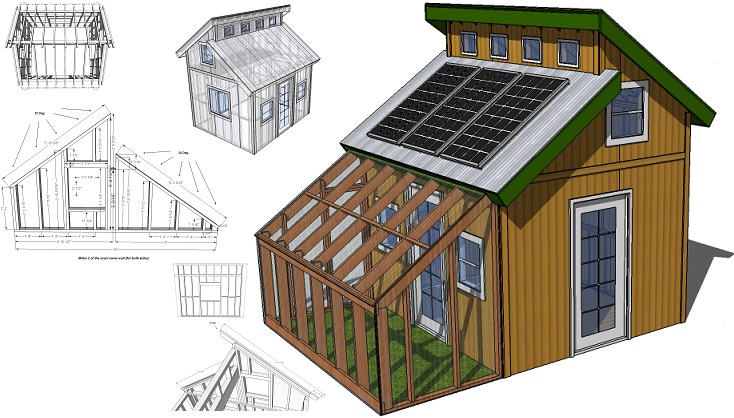
The central conflict in embracing eco-friendly home floor plans lies in the balance between sustainability and personal preferences. While the desire for a comfortable and aesthetically pleasing home remains strong, many individuals struggle to reconcile these aspirations with environmentally conscious design choices. This guide aims to bridge that gap, demonstrating that sustainable living can be both stylish and practical.
Target Audience:
This guide is designed for a broad audience, including:

- Homeowners: Individuals seeking to build a new home or renovate an existing one with a focus on sustainability.
- Architects and Designers: Professionals seeking to integrate eco-friendly principles into their design projects.
- Real Estate Developers: Companies aiming to develop sustainable communities and build environmentally conscious homes.
- Students and Professionals: Individuals interested in learning about sustainable architecture and design.
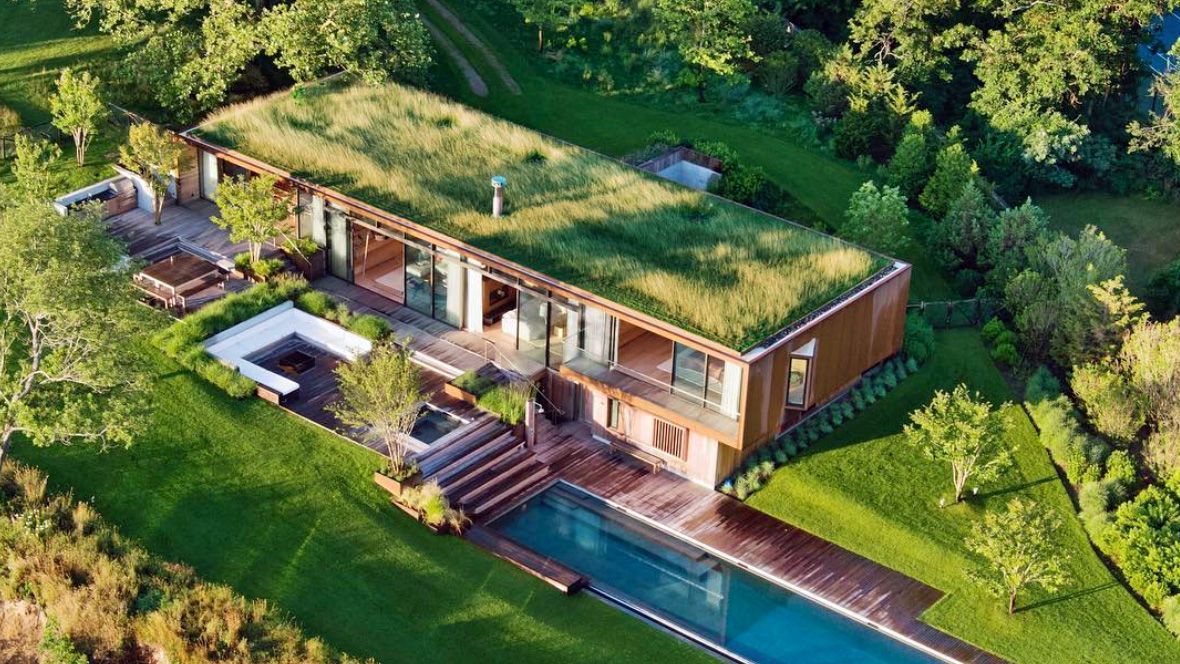



Key Features and Benefits:
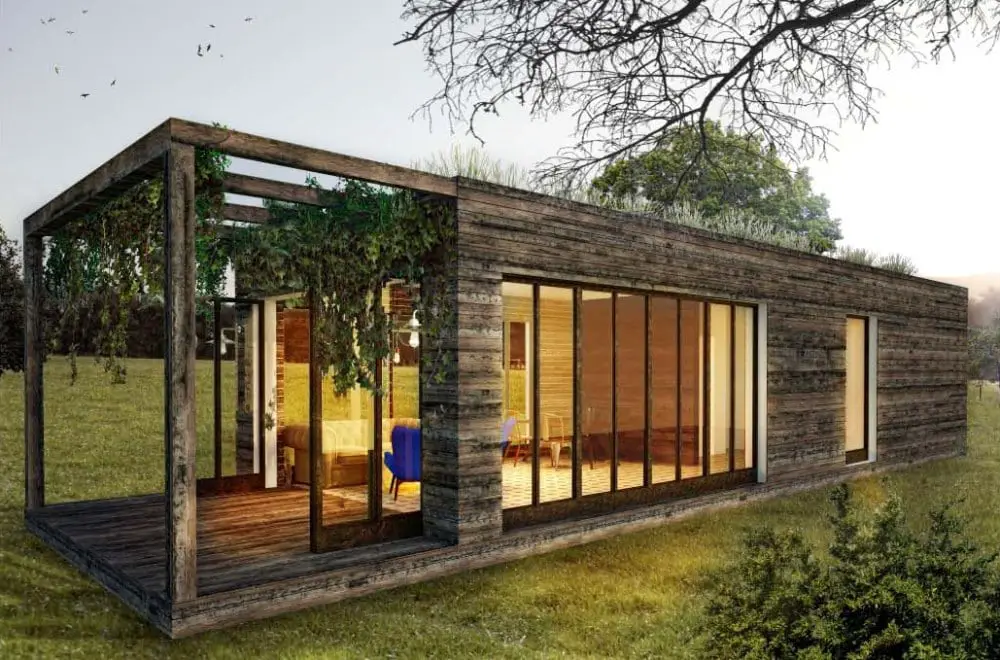

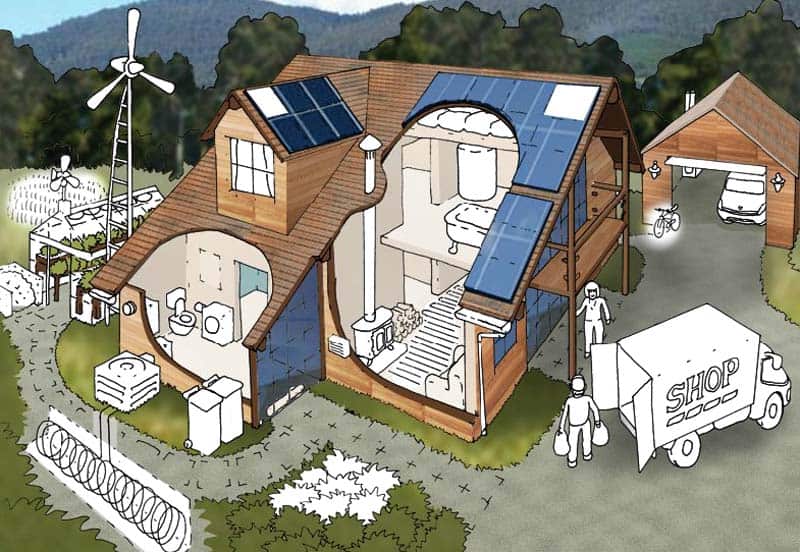
1. Energy Efficiency:
- Passive Solar Design: Utilizing natural sunlight for heating and lighting, reducing reliance on artificial sources.
- Proper Insulation: Minimizing heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, resulting in lower energy consumption.
- Efficient HVAC Systems: Implementing high-performance heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems for optimal energy usage.
- Smart Home Technology: Integrating smart devices and systems for automated energy management and optimization.


2. Water Conservation:
- Low-Flow Fixtures: Utilizing water-saving showerheads, faucets, and toilets to reduce water consumption.
- Rainwater Harvesting: Collecting and storing rainwater for irrigation and other non-potable uses.
- Greywater Systems: Recycling wastewater from showers and sinks for non-potable applications like watering gardens.
- Landscaping with Native Plants: Choosing drought-tolerant plants that require less water for optimal growth.
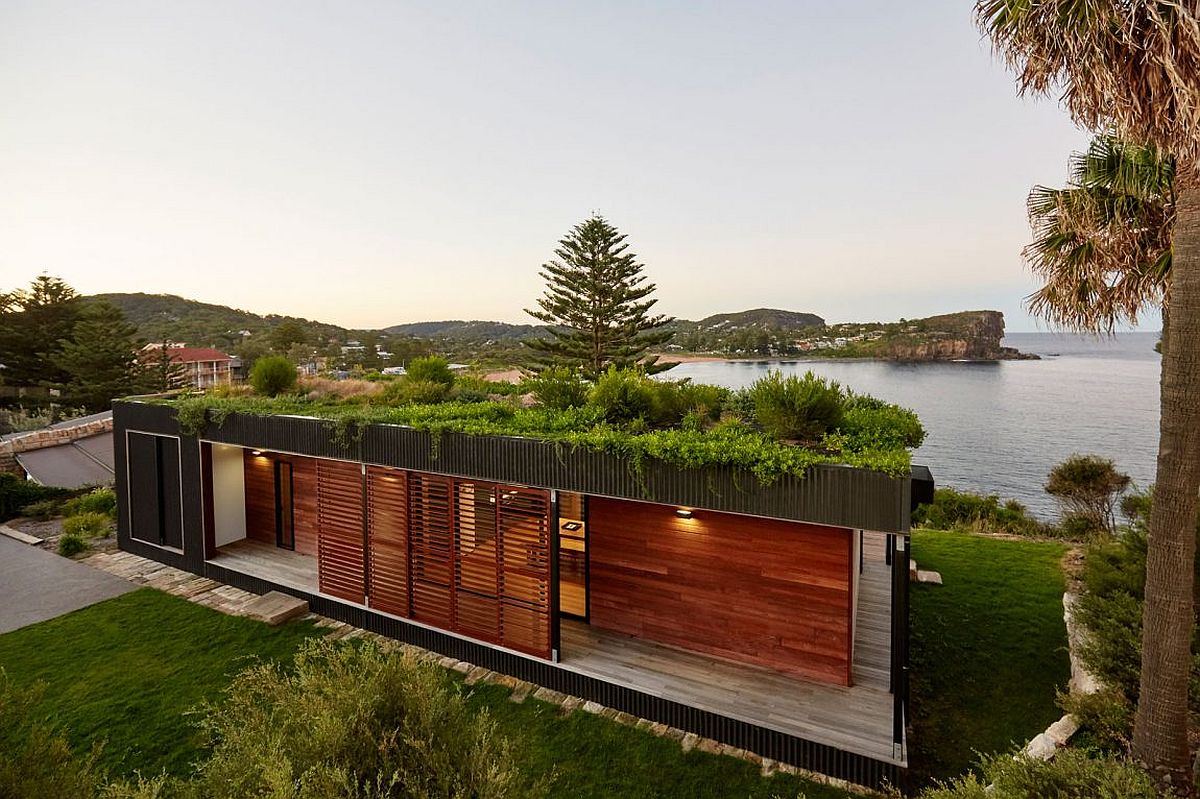





3. Material Sustainability:
- Locally Sourced Materials: Using building materials sourced from nearby regions to minimize transportation emissions.
- Recycled and Renewable Materials: Incorporating recycled materials like wood, concrete, and steel, and utilizing renewable resources like bamboo and cork.
- Low-VOC Paints and Finishes: Choosing paints and finishes with low volatile organic compound emissions for improved indoor air quality.
- Sustainable Building Practices: Employing construction methods that minimize waste, pollution, and energy consumption.
4. Indoor Air Quality:
- Natural Ventilation: Designing homes with cross-ventilation for optimal airflow and improved air circulation.
- Green Roofing: Installing vegetation on rooftops to improve insulation, reduce heat island effect, and enhance air quality.
- Indoor Plant Selection: Choosing plants known for their air-purifying qualities to enhance indoor air quality.
- Low-VOC Furniture and Furnishings: Selecting furniture and furnishings made from sustainable materials and with low VOC emissions.
5. Site Planning and Landscaping:
- Maximizing Natural Light: Orienting the home to optimize natural sunlight exposure for passive solar heating.
- Minimizing Site Disturbance: Preserving existing vegetation and minimizing soil disturbance during construction.
- Permeable Paving: Utilizing permeable paving materials for driveways and walkways to allow rainwater to infiltrate the ground.
- Native Landscaping: Selecting native plants for landscaping to create a sustainable and low-maintenance ecosystem.
Integrating Eco-Friendly Floor Plans into Your Story:
The core premise of the story revolves around a protagonist who is passionate about sustainable living and seeks to build their dream home with eco-friendly principles. The protagonist faces challenges in navigating the complexities of eco-friendly construction, overcoming skepticism from others, and balancing sustainability with personal preferences.
How Eco-Friendly Floor Plans Resonate with the Audience:
- Environmental Awareness: The story resonates with readers who are increasingly concerned about climate change and the impact of human activity on the environment.
- Sustainable Living: It appeals to individuals who are interested in living a more sustainable lifestyle and reducing their environmental footprint.
- Financial Savings: The story highlights the long-term cost savings associated with energy efficiency and resource conservation.
- Health and Well-being: It emphasizes the benefits of improved indoor air quality and a healthier living environment.
- Aesthetic Appeal: The story showcases how eco-friendly design can be both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
FAQs:
1. What are the costs associated with eco-friendly home floor plans?
While initial costs may be slightly higher due to the use of sustainable materials and technologies, the long-term savings from energy efficiency and reduced maintenance outweigh the initial investment. Government incentives and tax credits are often available to support eco-friendly construction projects.
2. Are eco-friendly homes less comfortable than traditional homes?
Absolutely not! Eco-friendly homes are designed to be comfortable and energy-efficient, with features like proper insulation, natural ventilation, and passive solar design that create a comfortable living environment.
3. Can I incorporate eco-friendly elements into an existing home?
Yes, many eco-friendly features can be retrofitted into existing homes. Simple upgrades like replacing old appliances with energy-efficient models, installing low-flow fixtures, and adding insulation can significantly improve sustainability.
4. What are the benefits of using locally sourced materials?
Using locally sourced materials reduces transportation emissions, supports local economies, and often leads to a more authentic and regional aesthetic.
5. How can I find a qualified architect or designer for my eco-friendly home project?
Look for architects and designers who are certified by organizations like the Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) or the Living Building Challenge. These certifications demonstrate a commitment to sustainable design principles.
Conclusion:
Eco-friendly home floor plans are not just a trend; they represent a paradigm shift in how we design and build our homes. By embracing sustainable principles, we can create living spaces that are both environmentally responsible and aesthetically pleasing. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the key features, benefits, and considerations for incorporating eco-friendly elements into your home’s blueprint. Remember, building a sustainable home is a journey, and every step you take towards a greener future is a step in the right direction.
