ERP Reporting: A Comprehensive Guide to Unleashing Value and Driving Action
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced business environment, where data-driven decision-making is paramount, ERP reporting has emerged as an indispensable tool for organizations seeking to gain a competitive edge. ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems consolidate data from various departments into a single, unified platform, providing a comprehensive view of an organization’s operations. ERP reporting harnesses this data to generate valuable insights, empowering businesses to make informed decisions, streamline processes, and optimize performance.
Understanding ERP Reporting
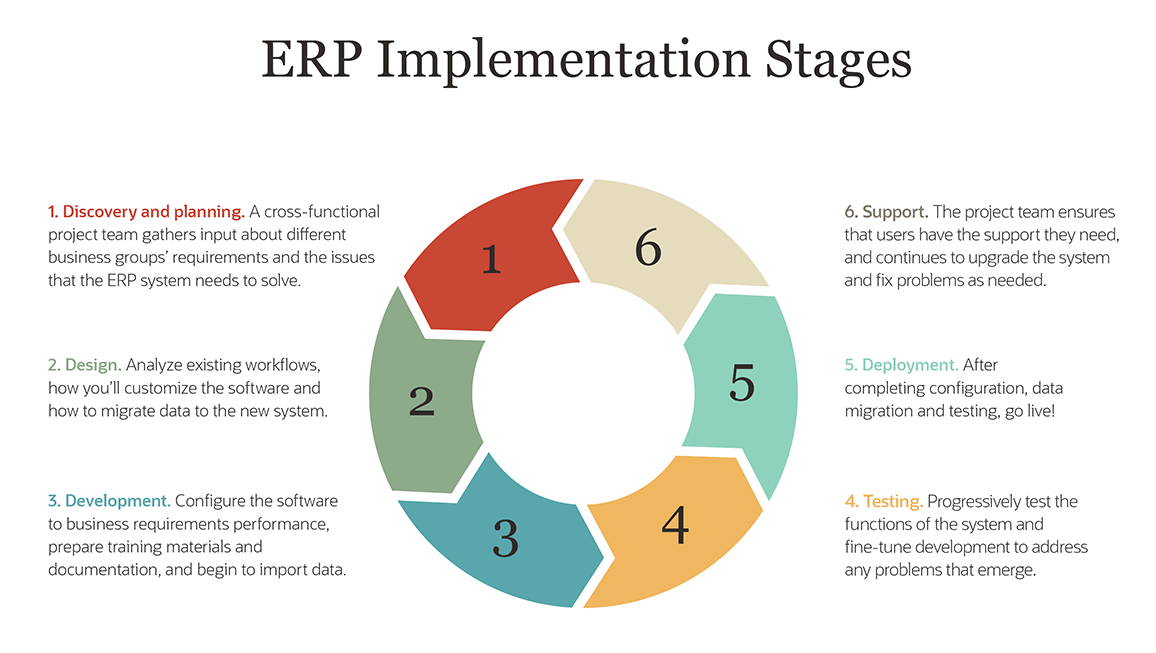
ERP reporting encompasses a wide range of reports that provide detailed information about an organization’s financial, operational, and performance metrics. These reports can be customized to meet the specific needs of different stakeholders, including executives, managers, and employees. Some common types of ERP reports include:
- Financial reports: Provide insights into an organization’s financial performance, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
- Operational reports: Track and analyze operational metrics, such as production output, inventory levels, and customer orders.
- Performance reports: Measure and evaluate key performance indicators (KPIs), such as sales growth, customer satisfaction, and employee productivity.
Benefits of ERP Reporting
ERP reporting offers numerous benefits to organizations, including:
- Improved decision-making: Provides real-time access to accurate and up-to-date data, enabling informed decision-making at all levels of the organization.
- Enhanced operational efficiency: Identifies bottlenecks and inefficiencies in processes, allowing organizations to streamline operations and reduce costs.
- Increased profitability: Provides insights into revenue and expense trends, helping organizations identify opportunities to increase profitability.
- Improved customer satisfaction: Enables organizations to track customer feedback and identify areas for improvement, leading to enhanced customer satisfaction.
- Reduced risk: Provides visibility into potential risks and vulnerabilities, allowing organizations to take proactive measures to mitigate them.
Challenges of ERP Reporting

While ERP reporting offers significant benefits, it also poses some challenges:
- Data accuracy: Ensuring the accuracy of ERP data is crucial for generating reliable reports. Data inconsistencies can lead to misleading insights and poor decision-making.
- Complexity: ERP systems can be complex, and generating meaningful reports requires a deep understanding of the system and its capabilities.
- Time-consuming: Creating and analyzing ERP reports can be time-consuming, especially for large organizations with complex data sets.
- Cost: Implementing and maintaining an ERP system can be expensive, and organizations need to carefully evaluate the costs and benefits before investing.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ERP Reporting
Advantages:
- Comprehensive view: Provides a consolidated view of all business operations, enabling a holistic understanding of the organization’s performance.
- Real-time insights: Offers access to real-time data, allowing organizations to respond quickly to changing market conditions.
- Improved collaboration: Facilitates collaboration between different departments by providing a shared platform for data and reporting.
- Enhanced accountability: Assigns clear ownership for data and reporting, improving accountability and performance.
- Data security: ERP systems typically have robust security measures in place to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.

Disadvantages:
- Data accuracy issues: Data inaccuracies can compromise the reliability of reports and lead to poor decision-making.
- Complexity: ERP systems can be complex, requiring specialized knowledge to generate meaningful reports.
- Time-consuming: Creating and analyzing ERP reports can be time-consuming, especially for large organizations.
- Cost: Implementing and maintaining an ERP system can be expensive, requiring careful cost-benefit analysis.
- Customization challenges: ERP systems may not always be fully customizable to meet the specific needs of an organization.
Summary of ERP Reporting
ERP reporting is a powerful tool that provides organizations with valuable insights into their financial, operational, and performance metrics. By leveraging ERP data, organizations can make informed decisions, streamline processes, and optimize performance. However, it is important to consider the challenges associated with ERP reporting, such as data accuracy, complexity, and cost. By carefully addressing these challenges, organizations can harness the full potential of ERP reporting to drive business success.
Q&A on ERP Reporting
Q1: What is the primary purpose of ERP reporting?
A1: The primary purpose of ERP reporting is to provide organizations with valuable insights into their financial, operational, and performance metrics, enabling informed decision-making and optimization of business processes.
Q2: What are the key benefits of ERP reporting?
A2: Key benefits include improved decision-making, enhanced operational efficiency, increased profitability, improved customer satisfaction, and reduced risk.
Q3: What are the common challenges associated with ERP reporting?
A3: Common challenges include ensuring data accuracy, managing complexity, addressing time-consuming processes, considering costs, and overcoming customization limitations.
Q4: How can organizations overcome the challenges of ERP reporting?
A4: Organizations can overcome challenges by investing in data quality initiatives, training staff on ERP systems, automating report generation, evaluating cost-benefit ratios, and customizing ERP systems to meet specific needs.
Q5: What are the different types of ERP reports?
A5: Common types include financial reports (income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements), operational reports (production output, inventory levels, customer orders), and performance reports (KPIs, sales growth, customer satisfaction).
Q6: What are the key considerations for implementing an ERP reporting system?
A6: Key considerations include defining reporting requirements, selecting an appropriate ERP system, ensuring data accuracy, training staff, and establishing a governance framework.
Q7: How can ERP reporting contribute to organizational growth?
A7: ERP reporting can contribute to organizational growth by providing insights for strategic planning, identifying opportunities for revenue growth, optimizing operations for efficiency, improving customer relationships, and mitigating risks.
Q8: What are the best practices for effective ERP reporting?
A8: Best practices include using standardized reporting formats, automating report generation, providing context and analysis, ensuring data security, and regularly reviewing and updating reports.
Q9: How can organizations measure the effectiveness of ERP reporting?
A9: Organizations can measure effectiveness by tracking report usage, evaluating the impact of reports on decision-making, assessing improvements in operational efficiency, and monitoring customer satisfaction and risk mitigation.
Q10: What are the emerging trends in ERP reporting?
A10: Emerging trends include cloud-based reporting, real-time analytics, artificial intelligence (AI)-driven insights, mobile reporting, and integrated reporting frameworks.
Q11: How can organizations prepare for the future of ERP reporting?
A11: Organizations can prepare by embracing cloud technologies, investing in data analytics capabilities, leveraging AI for insights, adopting mobile reporting solutions, and aligning reporting with strategic objectives.
Q12: What are the common pitfalls to avoid in ERP reporting?
A12: Common pitfalls include relying on outdated or inaccurate data, generating reports without clear objectives, overloading reports with unnecessary information, ignoring data security, and failing to communicate report findings effectively.
Q13: How can organizations ensure the accuracy and reliability of ERP reports?
A13: Organizations can ensure accuracy by implementing data validation processes, conducting regular data audits, training staff on data entry best practices, establishing clear data ownership, and leveraging data quality tools.
Conclusion
ERP reporting is a powerful tool that empowers organizations to make informed decisions, streamline processes, and optimize performance. By leveraging ERP data effectively, organizations can gain a competitive edge and achieve their business goals. However, it is important to address the challenges associated with ERP reporting and adopt best practices to ensure the accuracy, reliability, and effectiveness of reports. By embracing the full potential of ERP reporting, organizations can unlock valuable insights and drive business success.
Rebuttal
Some may argue that ERP reporting is too complex and time-consuming for organizations to implement effectively. However, with careful planning and execution, organizations can overcome these challenges and reap the significant benefits that ERP reporting offers. By investing in data quality, training staff, and automating report generation, organizations can streamline the ERP reporting process and make it an integral part of their decision-making and performance management strategies. The value of ERP reporting far outweighs the challenges, and organizations that embrace this powerful tool will be well-positioned for success in the modern business landscape.
