Federal Aid by State: Unveiling the Landscape of Financial Assistance
Introduction
The intricate tapestry of federal aid woven across the United States paints a vibrant picture of financial support, shaping the economic well-being of states and their citizens. Understanding the distribution and impact of federal aid is paramount for policymakers, economists, and anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of government assistance programs. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of federal aid by state, exploring its multifaceted features, benefits, advantages, and challenges.
Understanding Federal Aid
Federal aid encompasses a vast array of financial assistance provided by the federal government to state and local governments, as well as individuals and organizations. These funds are distributed through various programs and initiatives, each designed to address specific needs and objectives. The primary goal of federal aid is to promote economic growth, enhance social welfare, and mitigate regional disparities.
Types of Federal Aid
The federal government provides aid to states in a multitude of forms, including:
- Direct Grants: Funds provided to state governments for specific purposes, such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure development.
- Formula Grants: Grants distributed to states based on predetermined formulas that consider factors such as population, poverty levels, and economic conditions.
- Project Grants: Competitive grants awarded to states or local governments for specific projects or initiatives.
- Tax Expenditures: Reductions in federal taxes that provide financial benefits to states or individuals, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit.
- Loans and Loan Guarantees: Loans or guarantees provided by the federal government to support state or local infrastructure projects or economic development initiatives.
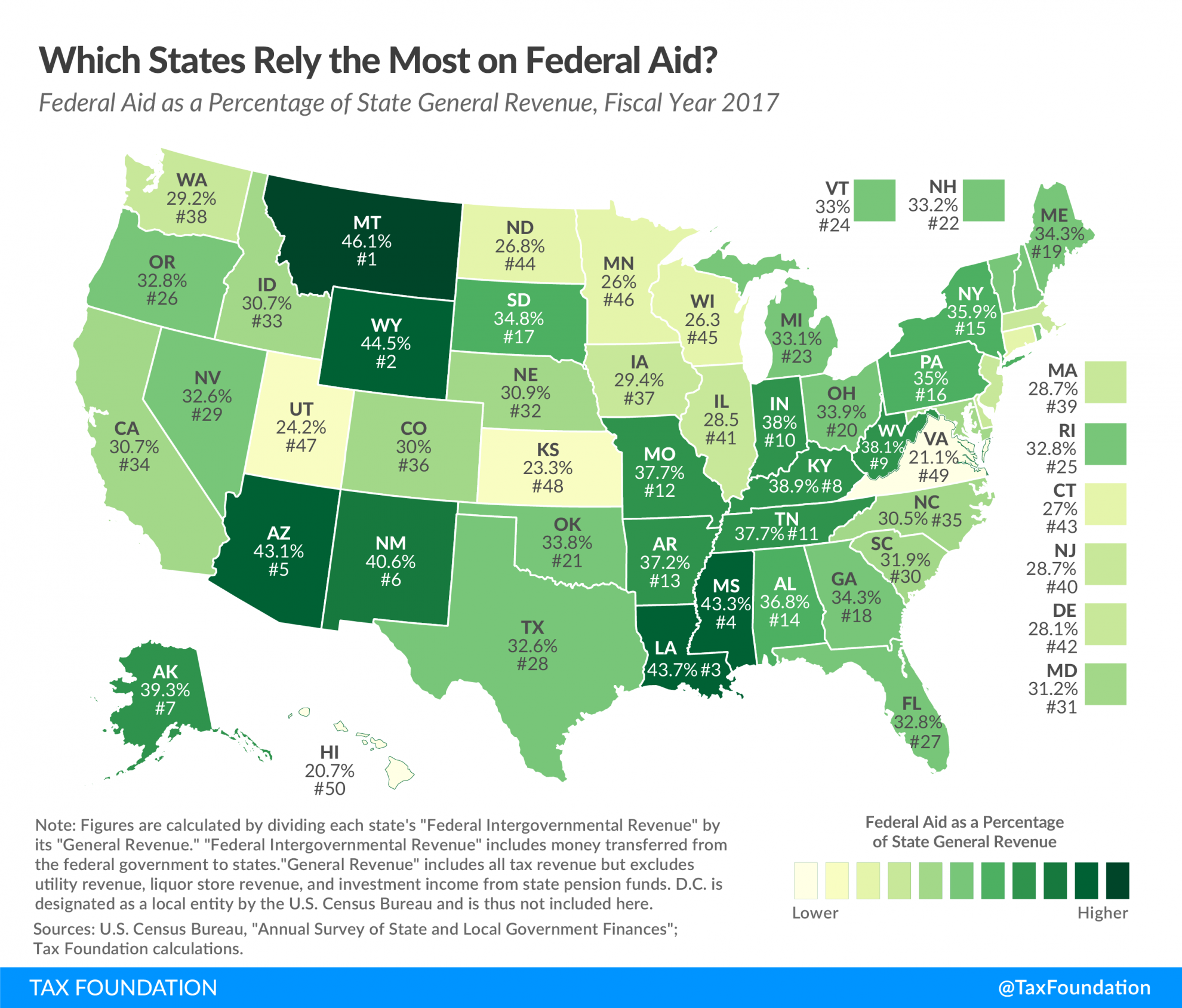
Distribution of Federal Aid
The distribution of federal aid among states is influenced by a complex array of factors, including:
- Population: States with larger populations typically receive more federal aid.
- Poverty Levels: States with higher poverty rates are eligible for additional federal assistance.
- Economic Conditions: States experiencing economic downturns may receive increased federal aid.
- Political Factors: The political affiliations of state and federal officials can influence the distribution of federal aid.
- Program Design: The specific criteria and formulas used to determine the allocation of federal aid can impact the distribution.

Benefits of Federal Aid
Federal aid provides numerous benefits to states, including:
- Economic Growth: Federal aid can stimulate economic growth by providing funding for infrastructure projects, job creation programs, and education initiatives.
- Improved Social Welfare: Federal aid supports social welfare programs that provide assistance to low-income families, the elderly, and individuals with disabilities.
- Reduced Regional Disparities: Federal aid helps to mitigate economic disparities between states by providing additional support to states with lower incomes or higher poverty rates.
- Enhanced Infrastructure: Federal aid can fund infrastructure projects that improve transportation, water systems, and energy efficiency.
- Increased Educational Opportunities: Federal aid supports education programs that provide access to quality education for students from all backgrounds.

Disadvantages of Federal Aid
While federal aid offers numerous benefits, it also has some potential drawbacks:
- Dependency: States may become overly reliant on federal aid, reducing their ability to generate revenue independently.
- Bureaucracy: Federal aid programs can be complex and bureaucratic, creating administrative burdens for states.
- Political Influence: The distribution of federal aid can be influenced by political factors, potentially leading to inequitable allocation.
- Crowding Out: Federal aid may crowd out state and local spending on similar programs, reducing the overall level of investment.
- Debt Accumulation: States may accumulate debt if they use federal aid to fund ongoing expenses rather than one-time investments.
Summary of Federal Aid by State
Federal aid plays a crucial role in shaping the economic and social landscape of the United States. By providing financial assistance to states, the federal government aims to promote economic growth, enhance social welfare, and reduce regional disparities. However, federal aid also comes with potential challenges, such as dependency, bureaucracy, and political influence. Understanding the distribution, benefits, and disadvantages of federal aid is essential for policymakers and citizens alike to make informed decisions about the allocation and use of these funds.
Q&A
-
What is the primary purpose of federal aid?
- To promote economic growth, enhance social welfare, and mitigate regional disparities.
-
What are the different types of federal aid?
- Direct grants, formula grants, project grants, tax expenditures, and loans/loan guarantees.
-
What factors influence the distribution of federal aid?
- Population, poverty levels, economic conditions, political factors, and program design.
-
What are the benefits of federal aid?
- Economic growth, improved social welfare, reduced regional disparities, enhanced infrastructure, and increased educational opportunities.
-
What are the disadvantages of federal aid?
- Dependency, bureaucracy, political influence, crowding out, and debt accumulation.
-
How can states maximize the benefits of federal aid?
- By carefully evaluating the needs of their state, developing strategic plans for the use of federal funds, and fostering collaboration with federal agencies.
Conclusion
Federal aid by state is a complex and multifaceted issue with far-reaching implications for the economic and social well-being of the United States. By understanding the distribution, benefits, and challenges associated with federal aid, policymakers, economists, and citizens can engage in informed discussions about the allocation and use of these funds. Federal aid has the potential to be a powerful tool for promoting economic growth, reducing poverty, and improving the quality of life for all Americans. It is essential that we continue to explore ways to maximize the benefits of federal aid while mitigating its potential drawbacks.
Closing Statement
The landscape of federal aid by state is constantly evolving, influenced by economic, political, and social factors. As we navigate the complexities of this issue, it is imperative that we approach it with a spirit of collaboration, transparency, and a commitment to ensuring that federal aid is used effectively and equitably to create a more prosperous and just society for all.
