Unlocking Manufacturing Efficiency: A Comprehensive Guide to ERP Modules
Introduction
In the fiercely competitive manufacturing landscape, efficiency is paramount. Manufacturers are constantly seeking ways to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance productivity. One powerful tool that has emerged as a game-changer in this pursuit is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) modules. These specialized software solutions integrate various aspects of manufacturing operations, providing a centralized platform for managing everything from production planning to inventory control. By embracing ERP modules, manufacturers can unlock a wealth of benefits, transforming their operations and gaining a competitive edge.
Understanding the Manufacturing ERP Landscape
ERP modules are designed specifically for the unique needs of manufacturing enterprises. They encompass a comprehensive suite of functionalities that address the core challenges faced by manufacturers, including:

-
Production Planning and Scheduling: ERP modules optimize production processes by enabling manufacturers to plan and schedule production activities effectively. They provide real-time visibility into production schedules, resource availability, and material requirements, allowing for efficient resource allocation and reduced lead times.
-
Inventory Management: ERP modules provide robust inventory management capabilities, ensuring accurate tracking of raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods. They enable manufacturers to maintain optimal inventory levels, minimize waste, and respond swiftly to changes in demand.
-
Quality Control: ERP modules integrate quality control processes into the manufacturing workflow, facilitating the identification and resolution of quality issues. They provide tools for tracking defects, conducting inspections, and implementing corrective actions, ensuring product quality and customer satisfaction.
-
Maintenance Management: ERP modules streamline maintenance activities by providing a centralized platform for managing equipment maintenance schedules, tracking maintenance history, and optimizing maintenance resources. This helps manufacturers prevent equipment breakdowns, reduce downtime, and extend asset lifespans.
-
Supply Chain Management: ERP modules connect manufacturers with their suppliers and customers, enabling seamless collaboration and efficient supply chain management. They facilitate real-time tracking of orders, inventory levels, and shipments, improving supply chain visibility and reducing lead times.
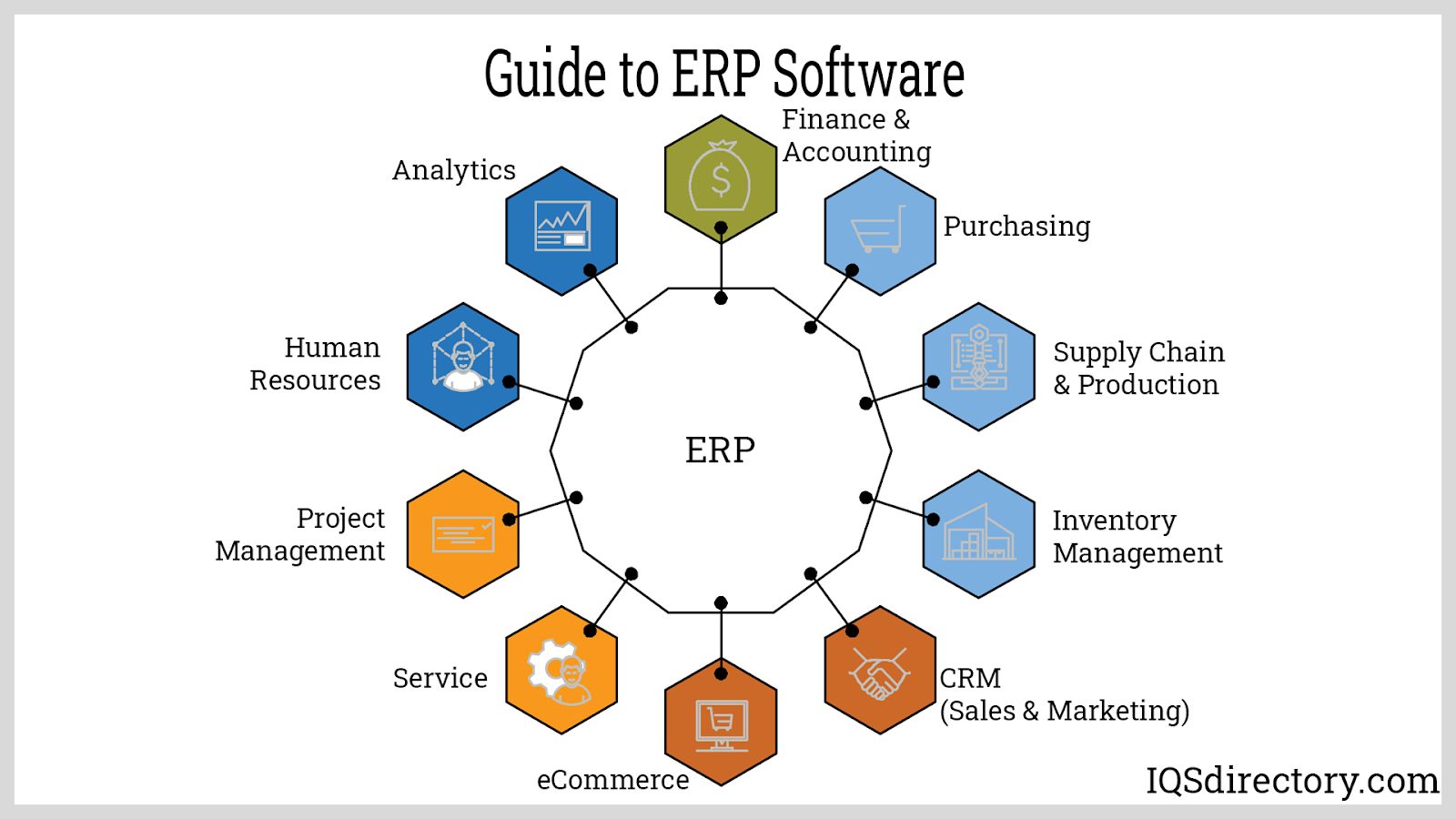
Advantages and Disadvantages of Manufacturing ERP Modules
Advantages:
-
Enhanced Efficiency: ERP modules streamline manufacturing operations, eliminating manual processes and reducing errors. This leads to increased productivity, reduced lead times, and lower operating costs.
-
Improved Visibility: ERP modules provide a centralized platform for managing manufacturing data, giving manufacturers real-time visibility into all aspects of their operations. This enables informed decision-making, proactive planning, and rapid response to changes in demand.
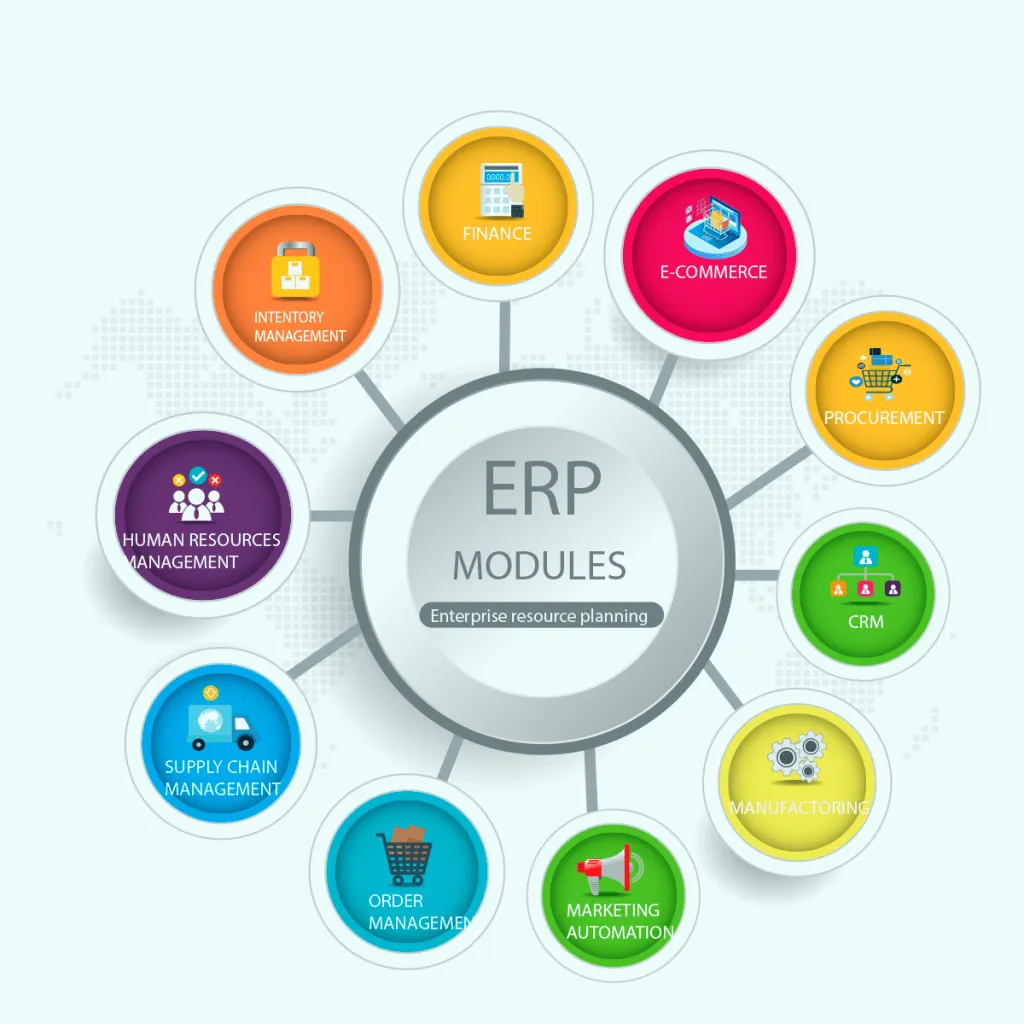
-
Increased Collaboration: ERP modules facilitate collaboration between different departments within a manufacturing enterprise. They break down silos and enable seamless communication, fostering a more cohesive and efficient work environment.
-
Reduced Waste: ERP modules optimize inventory management and production planning, minimizing waste and reducing the cost of goods sold. They help manufacturers identify and eliminate inefficiencies, leading to increased profitability.
-
Improved Quality: ERP modules integrate quality control processes into the manufacturing workflow, ensuring consistent product quality and reducing the risk of defects. They enable manufacturers to track and resolve quality issues quickly, enhancing customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
Disadvantages:
-
High Implementation Cost: Implementing ERP modules can be a significant investment, particularly for small and medium-sized manufacturers. The cost of software, hardware, and implementation services can be substantial.
-
Complexity: ERP modules are complex software systems that require careful planning and implementation. They may require significant training for users, and the transition process can be disruptive to operations.
-
Customization Challenges: ERP modules are often designed for a broad range of manufacturing industries. While they offer a comprehensive set of features, they may not be perfectly tailored to the specific needs of every manufacturer. Customization can be costly and time-consuming.
-
Data Security Concerns: ERP modules contain sensitive manufacturing data, making them a potential target for cyberattacks. Manufacturers must implement robust security measures to protect their data and prevent unauthorized access.
Key Pain Points of Manufacturing ERP Customers
Manufacturers face a range of pain points that ERP modules can effectively address:
-
Inefficient Production Processes: Manual processes and fragmented systems lead to errors, delays, and reduced productivity. Manufacturers struggle to optimize production schedules and meet customer demand efficiently.
-
Poor Inventory Management: Lack of real-time inventory visibility results in overstocking, stockouts, and increased carrying costs. Manufacturers find it challenging to maintain optimal inventory levels and respond to fluctuations in demand.
-
Lack of Collaboration: Siloed departments and fragmented communication hinder collaboration and information sharing. Manufacturers face difficulties in coordinating production, supply chain, and quality control activities effectively.
-
High Quality Control Costs: Manual quality control processes are prone to errors and inconsistencies. Manufacturers struggle to identify and resolve quality issues quickly, leading to increased rework and scrap costs.
-
Limited Supply Chain Visibility: Fragmented supply chain management systems make it difficult for manufacturers to track orders, inventory levels, and shipments across the supply chain. This lack of visibility hinders collaboration with suppliers and customers.
Key Considerations for Choosing Manufacturing ERP Modules
When selecting an ERP module, manufacturers should consider the following factors:
-
Industry Specificity: Choose an ERP module that is designed specifically for the manufacturing industry and addresses the unique challenges faced by manufacturers.
-
Functionality: Evaluate the functionality of the ERP module to ensure that it meets the specific requirements of your manufacturing operations. Consider features such as production planning, inventory management, quality control, and supply chain management.
-
Scalability: Choose an ERP module that can scale with your business as it grows. Consider the number of users, data volume, and future expansion plans.
-
Ease of Use: The ERP module should be user-friendly and intuitive, minimizing training time and reducing the risk of errors.
-
Implementation Cost: Consider the total cost of implementing the ERP module, including software, hardware, implementation services, and training.
-
Vendor Support: Choose a vendor that provides comprehensive support and training to ensure a successful implementation and ongoing maintenance of the ERP module.
Best Practices for Implementing Manufacturing ERP Modules
Successful implementation of ERP modules requires careful planning and execution:
-
Define Clear Goals: Establish clear objectives for implementing the ERP module, focusing on the specific pain points you aim to address.
-
Create a Project Plan: Develop a detailed project plan that outlines the implementation timeline, responsibilities, and milestones.
-
Engage Stakeholders: Involve all relevant stakeholders, including users, management, and IT staff, in the implementation process to ensure buy-in and support.
-
Choose the Right Vendor: Select a vendor that has experience in manufacturing ERP implementation and provides ongoing support and training.
-
Prepare Data: Clean and prepare your manufacturing data before implementing the ERP module to ensure data accuracy and integrity.
-
Test Thoroughly: Conduct thorough testing of the ERP module before going live to identify and resolve any issues.
-
Train Users: Provide comprehensive training to users on all aspects of the ERP module to ensure proficiency and adoption.
-
Monitor and Evaluate: Continuously monitor and evaluate the performance of the ERP module to identify areas for improvement and ensure ongoing success.
Conclusion
Manufacturing ERP modules are powerful tools that can transform manufacturing operations, driving efficiency, productivity, and profitability. By carefully considering the key pain points of your manufacturing enterprise and selecting the right ERP module, you can unlock a wealth of benefits. With proper planning, implementation, and ongoing support, ERP modules can empower manufacturers to gain a competitive edge and achieve operational excellence. Embrace the power of ERP technology and unlock the full potential of your manufacturing operations.
